[Tutorial]
We’re pleased to share new technical start guides to help engineers and system integrators get started with QEC-M-01 (EtherCAT MDevice) in combination with SANYO DENKI SANMOTION G servo amplifiers (EtherCAT) for real-time, high-performance motion control.

These guides provide a step-by-step setup process, practical coding examples, and integration tips, covering both CiA 402 CSP (Cyclic Synchronous Position) and PP (Profile Position) modes, so you can accelerate bring-up and reduce engineering time.
1. Highlights of the New Guide
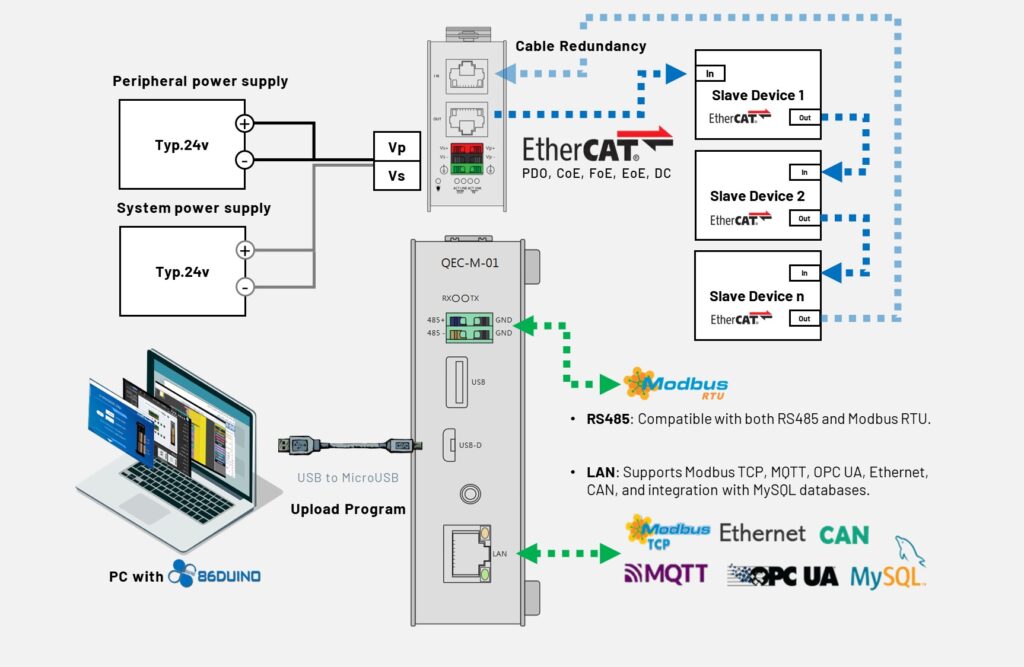
The QEC‑M‑01 is a compact and powerful EtherCAT MDevice equipped with a real-time multitasking architecture and integrated development tools. Powered by the open-source 86Duino IDE, it offers a simple yet powerful development platform for automation.
It enables precise and responsive control in demanding motion systems when paired with SANMOTION G servo Series products under the CiA402 CSP and PP Mode.
1.1 SANMOTION G (Why SANMOTION G?)
SANMOTION G is designed for compact, lightweight, and energy-saving AC servo applications, enabling high-speed/high-precision control and improved productivity and machining quality.
Key feature highlights:
- Speed frequency response up to 3.5 kHz (1.6× vs. conventional) via newly developed current control.
- Shorter positioning stabilization time (5.5 ms, ~1/3 of conventional) by friction/gravity detection & compensation.
- Max motor speed increased to 6500 min⁻¹ (from 6000 min⁻¹) and expanded output range.
- High-resolution encoder: 23-bit standard, up to 27-bit optional for high accuracy and stable positioning.
- Reliability & maintainability enhancements: remaining brake life estimation, surge current limit optimization, power monitoring, and EtherCAT communication quality diagnostics.
For EtherCAT users, SANMOTION G provides EtherCAT interface amplifiers (example: a 2-axis model lists Interface = EtherCAT). For detailed information, please refer to SANMOTION G series.
1.2 Advantages of the Start Guides
- Step-by-step setup guide:
Wiring, EtherCAT network bring-up, and recommended parameter checklist. - Programming examples (CSP / PP):
Practical code snippets and control flow examples to help you implement motion quickly. - Integration tips & troubleshooting:
Notes for typical field issues (drive enable sequence, alarm handling, EtherCAT quality checks, etc.).

2. Start Using QEC-M-01 with SANMOTION G AC Servo
Whether you are a novice or a professional developer, our guide provides the support you need to get started smoothly with QEC-M-01 and SANMOTION G AC Servo. Here are two example programs demonstrating PP mode and CSP mode.
2.1 Profile Position (PP) Mode
The following program sets the GADSA01AH24 into CiA402 Profile Position (PP) mode:
- EtherCAT Cycle Time: 1 millisecond.
- EtherCAT Mode: ECAT_SYNC.
The EthercatMaster object (“mdevice”) represents the QEC-M-01, while the EthercatDevice_CiA402 object (“motor”) represents the GADSA01AH24 driver
The example code is as follows:
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int pp_state = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Begin: ");
Serial.println(master.begin());
Serial.print("Slave: ");
Serial.println(motor.attach(0, master));
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PP_MODE);
// No PDO mapping by default, needs to be filled out by users.
// RxPDO mapping configuration.
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
// TxPDO mapping configuration.
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
Serial.print("Start: ");
Serial.println(master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC));
Serial.print("Enable: ");
Serial.println(motor.enable());
motor.pp_SetMotionProfileType(0); // Linear ramp (trapezoidal profile)
motor.pp_SetVelocity(100000000);
motor.pp_SetAcceleration(50000000);
motor.pp_SetDeceleration(50000000);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Pos: ");
Serial.println(motor.getPositionActualValue());
switch (pp_state)
{
case 0:
if (motor.pp_Run(1000000000) == 0)
pp_state++;
break;
case 1:
if (motor.pp_IsTargetReached())
pp_state++;
break;
case 2:
if (motor.pp_Run(-1000000000) == 0)
pp_state++;
break;
case 3:
if (motor.pp_IsTargetReached())
pp_state = 0;
break;
}
}2.2 Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP) mode
The following program sets the GADSA01AH24 into CiA402 Cyclic-Synchronous Position (CSP) mode:
- EtherCAT Cycle Time: 1 millisecond.
- EtherCAT Mode: ECAT_SYNC.
- Motion is generated inside a 1 ms cyclic callback by stepping a command position at a fixed rate (constant velocity).
The EthercatMaster object (“master”) represents the QEC-M-01, while the EthercatDevice_CiA402 object (“motor”) represents the GADSA01AH24 driver.
The example code is as follows:
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int32_t position = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback() {
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
motor.setTargetPosition(position += 10000);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.print("Begin: ");
Serial.println(master.begin());
Serial.print("Slave: ");
Serial.println(motor.attach(0, master));
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CSP_MODE);
// No PDO mapping by default, needs to be filled out by users.
// RxPDO mapping configuration.
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
// TxPDO mapping configuration.
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
Serial.print("Start: ");
Serial.println(master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC));
motor.setTargetPosition(position = motor.getPositionActualValue());
Serial.print("Enable: ");
Serial.println(motor.enable());
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Pos: ");
Serial.println(motor.getPositionActualValue());
delay(1000);
}If you are interested in learning more, click the link below to view the complete guide:
- CSP Mode:
- PP Mode:
We will continue to deliver robust and innovative EtherCAT automation platforms for smarter, faster, and more efficient control systems. We invite partners and developers to explore QEC solutions for your next innovative automation project.
For more info and sample requests, please write to info@icop.com.tw, call your nearest ICOP Branch, or contact our Worldwide Official Distributor.