2025.12.30, EtherCAT CiA 402 v1.2.
You can download the EtherCAT CiA 402 User Manual file 這裡.
1. 簡介
1.1 About QEC MainDevice (MDevice)
QEC MDevice is an EtherCAT MDevice compatible with 86Duino Coding IDE 501+. It offers real-time EtherCAT communication between the EtherCAT MDevice and the EtherCAT SubDevice. Except for the EtherCAT Library of 86Duino IDE, QEC MDevice also provides Modbus, Ethernet TCP/IP, CAN bus, etc., industrial communication protocols, and uses a rich high-level C/C++ programming language for rapid application development.
For additional QEC and EtherCAT details, please refer to the EtherCAT API 使用手冊.
1.1.1 What is 86Duino IDE?
86Duino 整合開發環境 (IDE) 軟體可以輕鬆編寫程式碼並上傳到 86Duino 開發板和 QEC 主站裝置。它可以在 Windows、Mac OS X 和 Linux 上運行。環境採用Java編寫,基於 Arduino IDE、Processing、DJGPP 等開源軟體,可從以下連結下載: https://www.qec.tw/zh/software/.

QEC MDevice’s software, 86Duino IDE, also offers a configuration utility: 86EVA, a graphic user interface tool for users to edit parameters for the EtherCAT network; its functions are as follows:
- EtherCAT SubDevice scanning
- 導入 ENI 文件
- 設定 EtherCAT 主站
- Configure EtherCAT SubDevice
For additional details, please refer to the 86EVA 使用手冊.
1.2 About EthercatDevice_CiA402
EthercatDevice_CiA402 is a generic CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice class designed to control any EtherCAT servo drive that supports the CiA 402 standard.
它提供了常用的CiA 402物件的存取函數以及多種CiA 402操作模式和功能組的操作函數,包括:
- 操作模式
- Profile Position (pp)
- Profile Velocity (pv)
- Profile Torque (tq)
- Homing (hm)
- Cyclic Synchronous Position (csp)
- Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (csv)
- Cyclic Synchronous Torque (cst)
- 功能組別
- Touch Probe
Implementation Directive for CiA402 Drive Profile.
Directive for using IEC 61800-7-201 within EtherCAT-based servo drives.
有關 CiA 402 的更多詳細信息,請參閱以下文件:
- CiA Draft Standard 402: CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
- CiA402 驅動設定檔的 ETG.6010 實作指令
- 目前使用的 CiA 402 驅動設備的使用手冊
EthercatDevice_CiA402 的類別關係如下圖所示:

- EthercatDevice_CiA402 inherits from _EthercatDevice_CommonDriver.
For more detailed information about EtherCAT Device Class, please refer to EtherCAT Library API User Manual – QEC.
1.2.1 Drives and Motion Control
The device control function block controls all functions of the drive (drive function and power section). It is divided into device control of the state machine and the operation mode function.
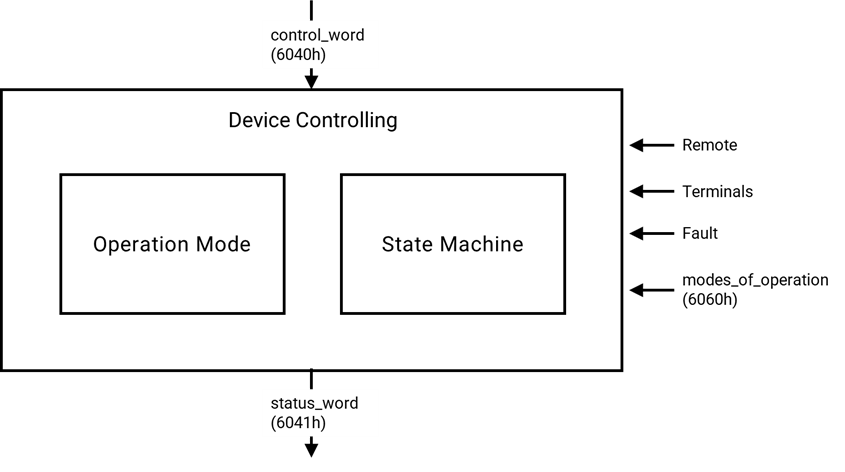
The controlword can control the state of the drive.
The state of the drive is shown in the statusword.
In remote mode, the device is controlled directly from the CANopen network by PDO and SDO.
The state machine is controlled externally by the controlword and external signals. The write access to the controlword is controlled by the optional hardware signal ‘Remote’. The state machine is also controlled by internal signals like faults and modes of operation.
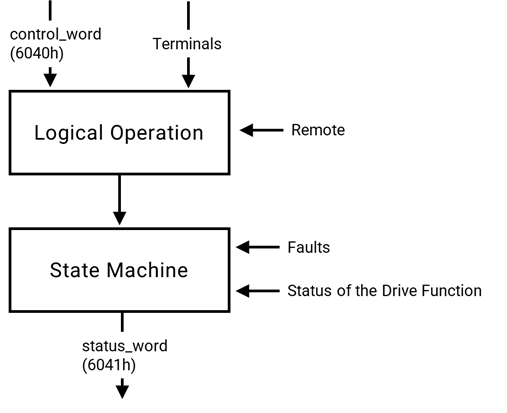
1.2.2 State machine
The state machine describes the device status and the possible control sequence of the drive. A single state represents a special internal or external behavior. The state of the drive also determines which commands are accepted. E.g. it is only possible to start a point-to-point move when the drive is in state OPERATION ENABLE.
States may be changed using the controlword and/or according to internal events. The current state can be read using the statusword.

State Description
| State | 描述 |
| Not Ready to Switch On | Drive is initializing or running a self-test. Brake (if present) is applied. Function disabled. |
| Switch On Disabled | Initialization complete, parameters set. High voltage not applied for safety. Function disabled. |
| Ready to Switch On | High voltage may be applied. Drive parameters can be modified. Function disabled. |
| Switched On | High voltage applied. Power amplifier is ready. Drive parameters can be modified. Function disabled. |
| Operation Enable | Fault detected. Drive function disabled. High-voltage switch-off depends on the application. |
| Quick Stop Active | Quick stop executed. Power removed, function disabled. To resume, send Enable Operation. |
| Fault Reaction Active | Fault detected. Quick stop is being executed. Power removed, function disabled. |
| Fault | Fault detected. Drive function disabled. High voltage switch-off depends on application. |
Notes:
- If a command is received that causes a change of state, this command must be processed completely and the new state attained before the next command can be processed.
- ‘Drive function is disabled’ implies no energy is supplied to the motor. This may be achieved by different manufacturers in different ways. Reference values are not processed.
- ‘Drive function is enabled’ implies that energy can be supplied to the motor. The reference values (torque, velocity, position) are processed.
- ‘Fault occurred’ implies that a fault in the drive has occurred. In this case, there is a transition to the state FAULT REACTION ACTIVE. In this state the device will execute a special fault reaction. After the execution of this fault reaction, the device will switch to the state FAULT. This state can only be left by the command ‘Fault Reset’, but only if the fault is not active anymore.
2. 函式
2.1 Initialization-related Functions
Initialization-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
2.2 Control-related Functions
Control-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
2.3 Operation-related Functions
Operation-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- setTargetPosition()
- setTargetVelocity()
- setTargetTorque()
- setProfileAcceleration()
- setProfileDeceleration()
- setMaxAcceleration()
- setMaxDeceleration()
- setMaxProfileVelocity()
- setMotionProfileType()
- setPositionWindow()
- setPositionWindowTime()
- setPositionOffset()
- setSoftwarePositionLimit()
- setFollowingErrorWindow()
- setPositionPolarity()
- setVelocityWindow()
- setVelocityWindowTime()
- setVelocityThreshold()
- setVelocityOffset()
- setMaxMotorSpeed()
- setVelocityPolarity()
- setTorqueOffset()
- setMaxTorque()
- setPositiveTorqueLimit()
- setNegativeTorqueLimit()
- setQuickStopDeceleration()
- setQuickStopOptionCode()
- setShutdownOptionCode()
- setDisableOperationOptionCode()
- setHaltOptionCode()
- setFaultReactionOptionCode()
- getErrorCode()
- getSupportedDriveModes()
- getMotorResolution()
- getPositionActualValue()
- getVelocityActualValue()
- getTorqueActualValue()
- getCurrentActualValue()
- getPositionDemandValue()
- getPositionDemandInternalValue()
- getPositionActualInternalValue()
- getAdditionalPositionActualValue()
- getFollowingErrorActualValue()
- getVelocityDemandValue()
- getTorqueDemandValue()
- getDigitalInputs()
2.4 Profile Position mode (pp) Related Functions
Profile Position mode (pp) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- pp_SetVelocity()
- pp_SetAcceleration()
- pp_SetDeceleration()
- pp_SetMotionProfileType()
- pp_Run()
- pp_IsTargetReached()
- pp_CheckFollowingError()
- pp_Halt()
- pp_Resume()
2.5 Profile Velocity mode (pv) Related Functions
Profile Velocity mode (pv) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- pv_SetAcceleration()
- pv_SetDeceleration()
- pv_SetMotionProfileType()
- pv_Run()
- pv_IsTargetReached()
- pv_CheckZeroSpeed()
- pv_CheckMaxSlippageError()
- pv_Halt()
- pv_Resume()
2.6 Profile Torque mode (tq) Related Functions
Profile Torque mode (tq) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- tq_SetTorqueSlope()
- tq_SetTorqueProfileType()
- tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent()
- tq_SetMotorRatedTorque()
- tq_Run()
- tq_IsTargetReached()
- tq_Halt()
- tq_Resume()
2.7 Homing mode (hm) Related Functions
Homing mode is the process by which a drive seeks the home position, also referred to as the datum, reference point, or zero point. This ensures that the motor starts from a known and repeatable position.
Homing can be achieved through various methods, typically using limit switches at the ends of travel or a home switch (zero point switch) in mid-travel. Many homing methods also utilize the index (zero) pulse train from an incremental encoder for precise positioning.
Homing mode (hm) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- hm_SetHomeOffset()
- hm_SetHomingMethod()
- hm_SetHomingSpeeds()
- hm_SetHomingAcceleration()
- hm_Run()
- hm_IsAttained()
- hm_Stop()
2.8 Function Group “Touch Probe” Related Functions
Touch Probe related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- enableTouchProbe1()
- enableTouchProbe2()
- disableTouchProbe1()
- disableTouchProbe2()
- isTouchProbe1ValueReady()
- isTouchProbe2ValueReady()
- readTouchProbe1Value()
- readTouchProbe2Value()
2.9 Low-level functions for mode-specific flow control
Low-level functions for mode-specific flow control related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- setHaltBit()
- isTargetReached()
- setModeSpecificBit4()
- setModeSpecificBit5()
- setModeSpecificBit6()
- checkModeSpecificBit12()
- checkModeSpecificBit13()
3. Example
3.1 Profile Position (pp) control
Implement position control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Position mode (pp).
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the positive direction.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the negative direction.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PP_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pp_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pp_SetVelocity(100000);
motor.pp_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pp_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
motor.pp_Run(100000, CIA402_PP_RELATIVE, true);
while (motor.pp_IsTargetReached() == 0);
motor.pp_Run(-100000, CIA402_PP_RELATIVE, true);
while (motor.pp_IsTargetReached() == 0);
}3.2 Profile Position (pp) control in cyclic callback
Implement position control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Position mode (pp) in cyclic callback.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the positive direction.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the negative direction.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 607Ah: Target position
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6064h: Position actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
#define STATE_SET_COMMAND (0)
#define STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET (1)
#define STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR (2)
#define STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED (3)
int state = STATE_SET_COMMAND;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
switch (state) {
case STATE_SET_COMMAND:
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetPosition(100000 * toggle - 100000 * !toggle);
motor.setModeSpecificBit6(true);
motor.setModeSpecificBit5(false);
motor.setModeSpecificBit4(true);
state = STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET;
break;
case STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET:
if (motor.checkModeSpecificBit12()) {
motor.setModeSpecificBit4(false);
state = STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR;
}
break;
case STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR:
if (motor.checkModeSpecificBit12() == 0)
state = STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED;
break;
case STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED:
if (motor.pp_IsTargetReached())
state = STATE_SET_COMMAND;
break;
}
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PP_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pp_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pp_SetVelocity(100000);
motor.pp_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pp_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.3 Profile Velocity (pv) control
Implement velocity control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Velocity mode (pv).
- Move in the positive direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
- Move in the negative direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PV_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pv_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pv_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pv_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
motor.pv_Run(1000);
while (motor.pv_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
motor.pv_Run(-1000);
while (motor.pv_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
}3.4 Profile Velocity (pv) control in cyclic callback
Implement velocity control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Velocity mode (pv).
- Move in the positive direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
- Move in the negative direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 60FFh: Target velocity
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 606Ch: Velocity actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int toggle = 0;
int cycle_count = 3000;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (++cycle_count < 3000)
return;
cycle_count = 0;
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetVelocity(1000 * toggle - 1000 * !toggle);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PV_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60FF0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x606C0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000);
motor.enable();
motor.pv_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pv_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pv_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.5 Profile Torque (tq) control
Implement torque control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Torque mode (tq).
- Maintain a positive torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
- Maintain a negative torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_TQ_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.tq_SetTorqueProfileType(0);
motor.tq_SetTorqueSlope(200);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedTorque(0);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent(0);
}
void loop() {
motor.tq_Run(50);
while (motor.tq_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
motor.tq_Run(-50);
while (motor.tq_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
}3.6 Profile Torque (tq) control in cyclic callback
Implement torque control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Torque mode (tq).
- Maintain a positive torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
- Maintain a negative torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 6071h: Target torque
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6077h: Torque actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int toggle = 0;
int cycle_count = 3000;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (++cycle_count < 3000)
return;
cycle_count = 0;
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetTorque(50 * toggle - 50 * !toggle);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_TQ_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60710010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60770010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000);
motor.enable();
motor.tq_SetTorqueProfileType(0);
motor.tq_SetTorqueSlope(200);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedTorque(0);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent(0);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.7 Homing (hm) operation
Initiate the homing method 33 operation on a CiA 402 compliant EtherCAT SubDevice.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_HOMING_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.hm_SetHomingMethod(CIA402_HM33);
motor.hm_SetHomeOffset(0);
motor.hm_SetHomingSpeeds(100, 20);
motor.hm_SetHomingAcceleration(100);
motor.hm_Run();
while (motor.hm_IsAttained() == CIA402_HM_RUNNING);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.8 Cyclic synchronous position (CSP) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target position is incremented by 1,000 units in each cycle.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 607Ah: Target position
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6064h: Position actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int32_t position = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
motor.setTargetPosition(position += 1000);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CSP_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetPosition(position = motor.getPositionActualValue());
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.9 Cyclic synchronous velocity (CSV) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target velocity is incremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches 3,000 units.
- The target velocity is decremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches -3,000 units.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 60FFh: Target velocity
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 606Ch: Velocity actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int32_t velocity = 0;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (abs(velocity) >= 3000)
toggle = !toggle;
velocity = velocity + toggle - !toggle;
motor.setTargetVelocity(velocity);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CSV_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60FF0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x606C0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetVelocity(0);
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.10 Cyclic synchronous torque (CST) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target torque is incremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches 50 units.
- The target torque is decremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches -50 units.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 6071h: Target torque
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6077h: Torque actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int16_t torque = 0;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (abs(torque) >= 50)
toggle = !toggle;
torque = torque + toggle - !toggle;
motor.setTargetTorque(torque);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CST_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60710010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60770010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetTorque(0);
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}附錄
A.1 錯誤代碼
對於大多數函式,回傳值小於零表示有錯誤,該值代表錯誤代碼。如果有錯誤代碼,您可以在下面找到錯誤原因和糾正措施。
| 定義 | 代碼 |
ECAT_SUCCESS | 0 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_INIT_FAIL | -100 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_GET_VERSION_FAIL | -101 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_VERSION_MISMATCH | -102 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_GENERIC_TRANSFER_INIT_FAIL | -103 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_DOWNLOAD_SETTINGS_FAIL | -200 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SET_DEVICE_SETTINGS_FAIL | -201 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_GROUP_INFO_FAIL | -202 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_MASTER_INFO_FAIL | -203 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_DEVICE_INFO_FAIL | -204 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SET_GROUP_SETTINGS_FAIL | -205 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_MAPPING_INIT_FAIL | -206 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_INTERRUPT_INIT_FAIL | -207 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACTIVE_FAIL | -208 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_INITCMDS_FAIL | -209 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NO_DEVICE | -210 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_INIT_FAIL | -300 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_REQUEST_FAIL | -301 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_BUSY | -302 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_TIMEOUT | -303 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_ERROR | -304 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_WRONG_STATUS | -405 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GENERIC_SEND_FAIL | -400 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GENERIC_RECV_FAIL | -401 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_BEGIN | -1000 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WRONG_BUFFER_SIZE | -1001 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_REDUNDANCY_NO_DC | -1002 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAIL | -1003 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_OSLAYER_INIT_FAIL | -1004 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NIC_INIT_FAIL | -1005 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_BASE_INIT_FAIL | -1006 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CIA402_INIT_FAIL | -1007 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SETUP_PDO_FAIL | -1008 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SCAN_NETWORK_FAIL | -1009 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_START_MASTER_FAIL | -1010 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CYCLETIME_TOO_SMALL | -1011 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_DUMP_OUTPUT_PDO_FAIL | -1012 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CONFIG_DEVICE_FAIL | -1013 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CONFIG_MAPPING_FAIL | -1014 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WAIT_BUS_SYNC_TIMEOUT | -1015 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WAIT_MASTER_SYNC_TIMEOUT | -1016 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CYCLIC_START_FAIL | -1017 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WRONG_BUFFER_POINTER | -1018 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_INIT_FAIL | -1050 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_MISMATCH | -1051 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_STOPPED | -1100 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_STARTED | -1101 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_PREOP | -1102 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_SAFEOP | -1103 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_OP | -1104 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_II_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1200 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_IP_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1201 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_PS_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1202 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SO_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1203 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_EXIST | -2000 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_ATTACH | -2001 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_MAILBOX | -2002 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_DC | -2003 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_WRONG_INPUT | -2004 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAIL | -2005 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID_MISMATCH | -2006 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PRODUCT_CODE_MISMATCH | -2007 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_SUCH_FUNCTION | -2008 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FUNCTION_NOT_INIT | -2009 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_BUSY | -2010 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_TIMEOUT | -2011 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_DATA | -2012 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_SII_READ_FAIL | -2100 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_SII_WRITE_FAIL | -2101 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PDO_NOT_EXIST | -2200 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PDO_OUT_OF_RANGE | -2201 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2300 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2310 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_TIMEOUT | -2311 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_ERROR | -2312 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL | -2313 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_READ_FAIL | -2314 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_WRITE_FAIL | -2315 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_SDO_NOT_SUPPORT | -2400 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_SDO_INFO_NOT_SUPPORT | -2401 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_BUSY | -2410 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2411 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_TIMEOUT | -2412 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_ERROR | -2413 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NOT_EXIST | -2500 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_ADD_FAIL | -2501 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_TYPE_MISMATCH | -2502 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_MODE_SUPPORT | -2503 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_WRONG_MODE | -2504 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_MODE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2505 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_CHANGE_WRONG_STATE | -2506 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_WRITE_OBJECT_FAIL | -2507 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_SUCH_TOUCH_PROBE | -2580 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_SUCH_TOUCH_PROBE_SOURCE | -2581 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2600 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_NO_SUCH_PORT | -2601 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_TOO_MUCH_CONTENT | -2602 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_BUSY | -2610 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2611 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_TIMEOUT | -2612 |
ECAT_ERR_GROUP_WRONG_INPUT | -3000 |
ECAT_ERR_GROUP_NOT_ATTACH | -3001 |
A.2 錯誤描述與修正措施
關於錯誤代碼說明和糾正措施。
A.3 SDO Abort Code
ETG.1000.6 中定義的 CoE SDO Abort Codes:
| 值 | 含義 |
| 0x05030000 | 切換位元未變更。 |
| 0x05040000 | SDO 通訊協定逾時。 |
| 0x05040001 | 用戶端/伺服器命令指定符號無效或未知。 |
| 0x05040005 | 超出記憶體。 |
| 0x06010000 | 不支援物件的存取。 |
| 0x06010001 | 嘗試讀取只能寫入的物件。 |
| 0x06010002 | 嘗試寫入唯讀物件。 |
| 0x06010003 | 子索引無法寫入,SI0 必須為 0 才能進行寫入存取。 |
| 0x06010004 | 不支援 SDO 完全存取長度可變的物件,例如 ENUM 物件類型。 |
| 0x06010005 | 物件長度超出信箱大小。 |
| 0x06010006 | 物件對應至 RxPDO,SDO 下載受阻。 |
| 0x06020000 | 物件不存在於物件目錄中。 |
| 0x06040041 | 物件無法對應至 PDO。 |
| 0x06040042 | 要對應的物件數量和長度會超過 PDO 的長度。 |
| 0x06040043 | 一般參數不相容。 |
| 0x06040047 | 裝置內部不相容。 |
| 0x06060000 | 由於硬體錯誤,存取失敗。 |
| 0x06070010 | 資料類型不符,服務長度參數不符。 |
| 0x06070012 | 資料類型不符,服務長度參數太高。 |
| 0x06070013 | 資料類型不符,服務長度參數太低。 |
| 0x06090011 | 子索引不存在。 |
| 0x06090030 | 超出參數值範圍(僅限寫入存取)。 |
| 0x06090031 | 寫入的參數值太高。 |
| 0x06090032 | 寫入的參數值太低。 |
| 0x06090036 | 最大值小於最小值。 |
| 0x08000000 | 一般性錯誤。 |
| 0x08000020 | 資料無法傳輸或儲存至應用程式。 注意: 這是一般的中止代碼,無法確定原因的詳細資訊。建議使用其中一個更詳細的中止代碼。(0x08000021, 0x08000022) |
| 0x08000021 | 由於本機控制,資料無法傳輸或儲存至應用程式。 注意:「本機控制 」是指應用程式特有的原因。不是指 ESM 特有的控制。 |
| 0x08000022 | 由於目前的裝置狀態,資料無法傳輸或儲存至應用程式。 注意:「裝置狀態」是指 ESM 狀態。 |
| 0x08000023 | 物件字典動態產生失敗或沒有物件字典。 |
A.4 Data Type
ETG.1000.6 中定義的基本資料類型:
| 索引 (十六進制) | 物件類型 | 名稱 |
| 0001 | DEFTYPE | BOOLEAN |
| 0002 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER8 |
| 0003 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER16 |
| 0004 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER32 |
| 0005 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED8 |
| 0006 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED16 |
| 0007 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED32 |
| 0008 | DEFTYPE | REAL32 |
| 0009 | DEFTYPE | VISIBLE_STRING |
| 000A | DEFTYPE | OCTET_STRING |
| 000B | DEFTYPE | UNICODE_STRING |
| 000C | DEFTYPE | TIME_OF_DAY |
| 000D | DEFTYPE | TIME_DIFFERENCE |
| 000F | DEFTYPE | DOMAIN |
| 0010 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER24 |
| 0011 | DEFTYPE | REAL64 |
| 0012 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER40 |
| 0013 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER48 |
| 0014 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER56 |
| 0015 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER64 |
| 0016 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED24 |
| 0018 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED40 |
| 0019 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED48 |
| 001A | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED56 |
| 001B | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED64 |
| 001D | DEFTYPE | GUID |
| 001E | DEFTYPE | BYTE |
| 002D | DEFTYPE | BITARR8 |
| 002E | DEFTYPE | BITARR16 |
| 002F | DEFTYPE | BITARR32 |
A.5 About CiA DSP 402
The CiA DSP 402 represents the standardized CANopen device profile for digital controlled motion products like servo controllers, frequency converters or stepper motors.
All the devices mentioned above use communication techniques which conform to those described in the CiA Draft Standard DS 301 (CANopen Application Layer and Communication Profile). This document should be consulted in parallel to CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
REFERENCES
- ISO 7498, 1984, Information Processing Systems – Open Systems Interconnection – Basic Reference Model
- ISO 11898-1, 1999, Road Vehicles, Interchange of Digital Information – Controller Area Network (CAN) for high-speed Communication
- CiA DS 301, CANopen Application Layer and Communication Profile, Version 4.02, February 2002
- CiA DS 401, CANopen Device Profile I/O Modules, Version 2.1, May 2002
- DRIVECOM Profil Antriebstechnik/Profil 21
- DRIVECOM Profil Antriebstechnik/Servo 22, Jan. 1994
DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATION
| Abbr. | 定義 |
| CAN | Controller Area Network |
| CiA | CAN in Automation e. V. |
| COB | Communication Object (CAN message). A unit of transportation in a CAN network. Data must be sent across a network inside a COB. |
| COB-ID | COB-Identifier. Identifies a COB uniquely in a network. The identifier determines the priority of that COB in the MAC sub-layer too. |
| PDO | Process Data Object. Object for data exchange between several devices. |
| SDO | Service Data Object. Peer-to-peer communication with access to the object dictionary of a device. |
| pp | Profile Position Mode |
| pv | Profile Velocity Mode |
| vl | Velocity Mode |
| hm | Homing Mode |
| ip | Interpolated Position Mode |
| tq | Profile Torque Mode |
| all | Mandatory for all modes |
| ce | Common entries in the object dictionary |
| dc | Device Control |
| pc | Position Control Function |
A.6 Object Dictionary Entries
All information follows the CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
A.7 Homing Methods
All information follows the CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
86Duino 參考的文本是根據 知識共享署名-相同方式分享 3.0 許可證,部分文本是從 Arduino 參考 修改的。 參考中的代碼示例已發佈到公共領域。
For more info and sample requests, please write to info@icop.com.tw,致電離您最近的 ICOP分公司,或聯絡我們的 全球官方經銷商。