EtherCAT MDevice Software Performance
When using an EtherCAT network for Fieldbus, good performance is a decisive factor, primarily correlating to a short cycle time (around 1kHz or faster). Since the performance of an EtherCAT Network can be attributed to the EtherCAT MDevice, its software should be able to support shorter cycle times, a large amount of cyclic process data, as well as handle many EtherCAT devices.
EtherCAT MDevice Software Requires:
- 高性能和實時乙太網路驅動 (link layer)
- 獨立於操作系統外的循環處理 (Cyclic processing)
- 支持不間斷運行(無內部任務)
- 支持在 CPU 任務中對處理時間進行切分
An EtherCAT MDevice software must manage and provide parameter settings to reserve sufficient computing power for the actual application and the specified timing on the bus to reduce this peak load.
EtherCAT 網路的關鍵影響變量
基於應用差異,以下因素是影響 EtherCAT 網路的關鍵領域:
- SubDevice Numbers
- SubDevice Types
- 循環週期數據大小
- 週期時間
- EtherCAT MDevice features or capabilities (Distributed Clocks, Cable Redundancy, etc.)
- 必要的計算時間
As we will demonstrate, QEC’s software, 86Duino IDE, takes all the variables into consideration and manages numerous systems using only 10-20% of the available CPU time.
測量
To compute the time consumption of all process paths on the EtherCAT MDevice software, 86Duino IDE, we carried out performance measurements on QEC-M systems. To confirm their Real-time performance was measured correctly and precisely, different cycle time options were tested.
為了得到可靠的測量值,測量是需要通過實際的 EtherCAT 網路配置來進行現場演示。這些測量可以使用86Duino IDE EtherCAT 函式庫示例進行,無需額外的操作或設備。在這些演示應用程序中,各個主站工作功能的執行時間(最小、最大和平均)以及被計算出來週期時間,將會保存到日誌文件中(或打印到控制台)。
範例中的測量函數
在 86Duino IDE 中,EtherCAT 網路循環部分是高度集成的,由某些具有特定任務的功能組成,由於其嚴格的劃分,不會與其他功能發生交互。基於這一特點,我們可以測量這些主幀 (Frames)的時間消耗,進一步確保循環過程的準確性。
这些任务包括:

在前一個 EtherCAT 幀中的接收數據(輸入),首先在 "Process Inputs" 任務中被更新。"User Application" 任務將獲取其新接收的數據,計算數據(輸出),並通過 "Write Outputs" 任務將其發送至網絡。
EtherCAT 幀可以直接透過內存訪問(DMA)通過網路總線。這意味著數據可以在不加載 CPU 的情況下進行傳輸,也可以在返回主站時不間斷地自動接收,或者在使用物理網絡時發送出去。
In the “State Management and Acyclic Send (SMAS)” task, the MDevice state machine and each slave state machine are executed. All Subdevice states are transferred from INIT to OPERATIONAL during the initial start-up process. The acyclic mailbox communications require another frame with slave-specific commands for reading and writing to the slave. Moreover, to handle these acyclic mailbox communications like CoE, the state machines are needed in regular operation.
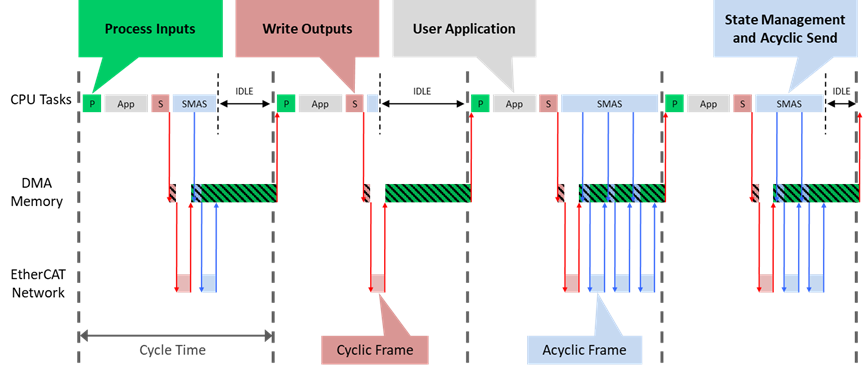
範例
測量結果將在 setup() 函數中打印到終端顯示。
[benchmark.ino]
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_Generic slave;
#define WAIT_TIME_MS (10000)
void setup()
{
EthercatPerfMeasurement perf;
unsigned long pretime;
unsigned long sdoValue, sdoCount = 0;
Serial.begin(115200);
master.configPerfMeasurement(true);
master.begin();
slave.attach(0, master);
master.start(1000000);
pretime = millis();
while (millis() - pretime 0)
sdoCount++;
}
master.getPerfMeasurement(&perf);
Serial.print("[C] Cycle Time (min/avg/max) [usec]: ");
Serial.print(perf.CycleTime.MinimumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.print(perf.CycleTime.AverageNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.println(perf.CycleTime.MaximumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print("[P] Process Inputs (min/avg/max) [usec]: ");
Serial.print(perf.ReceiveCyclicFrame.MinimumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.print(perf.ReceiveCyclicFrame.AverageNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.println(perf.ReceiveCyclicFrame.MaximumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print("[S] Write Outputs (min/avg/max) [usec]: ");
Serial.print(perf.SendCyclicFrame.MinimumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.print(perf.SendCyclicFrame.AverageNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.println(perf.SendCyclicFrame.MaximumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print("[SMAS] State Management and Acyclic Send (min/avg/max) [usec]: ");
Serial.print(perf.ProcessAcyclicFrame.MinimumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.print(perf.ProcessAcyclicFrame.AverageNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print(" / ");
Serial.println(perf.ProcessAcyclicFrame.MaximumNs / 1000.0);
Serial.print("The throughput of SDO commands. [SDO/sec]: ");
Serial.println((double)(sdoCount * 1000) / WAIT_TIME_MS);
master.stop();
master.end();
}
void loop() {}測量結果
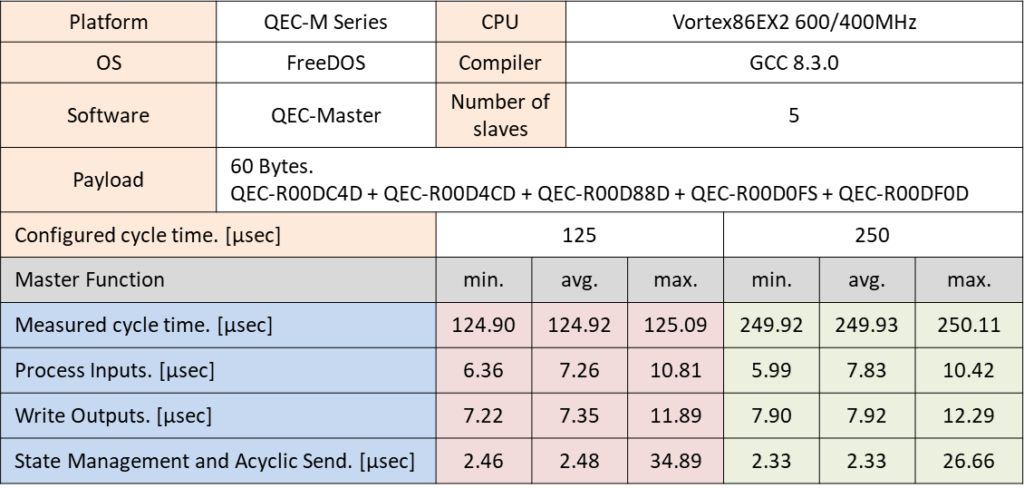
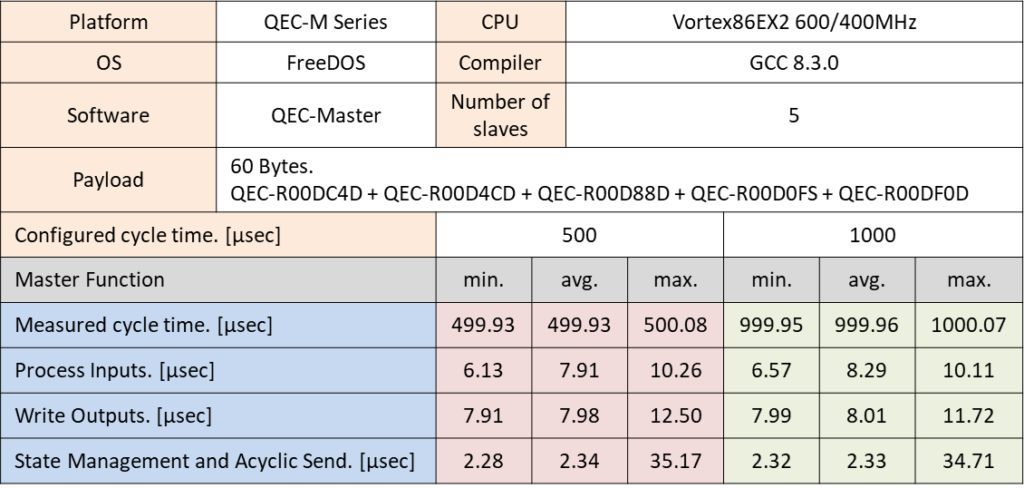
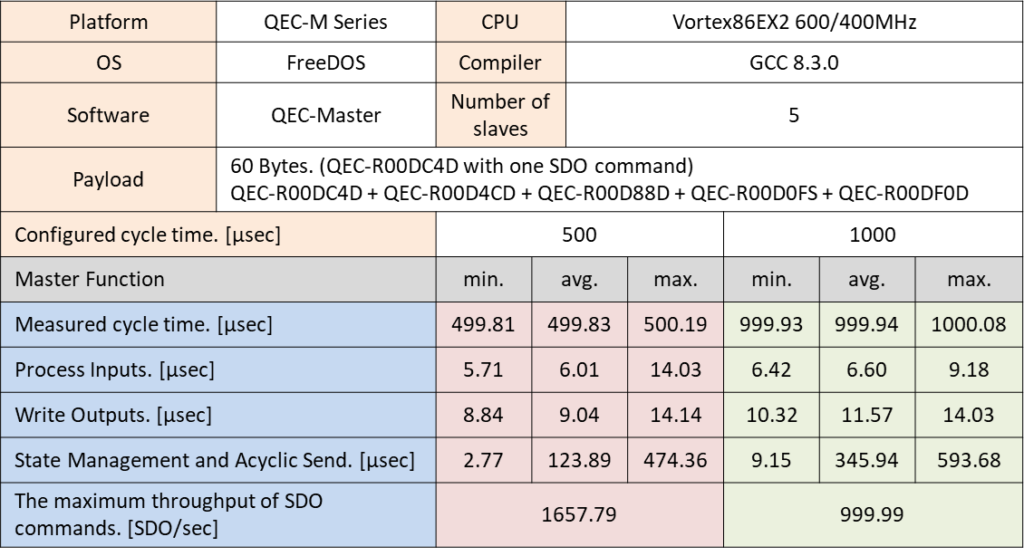
The following results were performed with 5 different devices of QEC Digital I/O SubDevices with different cycle times, 125, 250, 500, and 1000 µsec. The SDO commands were processed in the SMAS task and were also measured by the maximum throughput in cycle time.
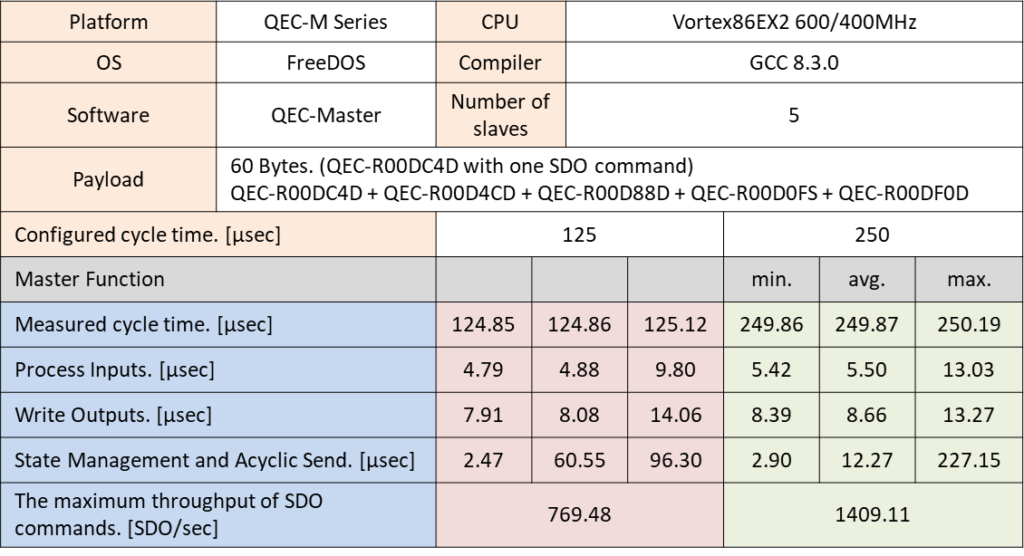
使用 SDO 命令:
影片
請繼續關注 QEC 的更多項目!
如果您有任何疑問/疑問,請隨時發表評論!