2025.12.30, EtherCAT CiA 402 v1.2.
You can download the EtherCAT CiA 402 User Manual file ここ.
1. 概要
1.1 About QEC MainDevice (MDevice)
QEC MDevice is an EtherCAT MDevice compatible with 86Duino Coding IDE 501+. It offers real-time EtherCAT communication between the EtherCAT MDevice and the EtherCAT SubDevice. Except for the EtherCAT Library of 86Duino IDE, QEC MDevice also provides Modbus, Ethernet TCP/IP, CAN bus, etc., industrial communication protocols, and uses a rich high-level C/C++ programming language for rapid application development.
For additional QEC and EtherCAT details, please refer to the EtherCAT ライブラリ API ユーザーマニュアル.
1.1.1 What is 86Duino IDE?
86Duino統合開発環境(IDE)ソフトウェアを使えば、86DuinoボードとQEC Mainデバイスへのコード記述とアップロードが簡単に行えます。Windows、Mac OS やLinuxで動作します。この環境はJavaで記述されており、Arduino IDE、Processing、DJGPPなどのオープンソースソフトウェアをベースにしています。これらのソフトウェアは以下からダウンロードできます。 https://www.qec.tw/software/.

QEC MDevice’s software, 86Duino IDE, also offers a configuration utility: 86EVA, a graphic user interface tool for users to edit parameters for the EtherCAT network; its functions are as follows:
- EtherCAT SubDevice scanning
- ENIファイルのインポート
- EtherCAT Mainデバイスの設定
- Configure EtherCAT SubDevice
For additional details, please refer to the 86EVA User Manual.
1.2 About EthercatDevice_CiA402
EthercatDevice_CiA402 is a generic CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice class designed to control any EtherCAT servo drive that supports the CiA 402 standard.
一般的に使用される CiA 402 オブジェクトへのアクセス機能と、次のようないくつかの CiA 402 操作モードおよび機能グループの操作機能を提供します。
- Operation Modes
- Profile Position (pp)
- Profile Velocity (pv)
- Profile Torque (tq)
- Homing (hm)
- Cyclic Synchronous Position (csp)
- Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (csv)
- Cyclic Synchronous Torque (cst)
- Function Groups
- Touch Probe
Implementation Directive for CiA402 Drive Profile.
Directive for using IEC 61800-7-201 within EtherCAT-based servo drives.
CiA 402 の詳細については、次のドキュメントを参照してください。
- CiA Draft Standard 402: CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
- ETG.6010 Implementation Directive for CiA402 Drive Profile
- 現在使用されているCiA 402ドライブデバイスのユーザーマニュアル
EthercatDevice_CiA402 のクラス関係は次の図に示されています。

- EthercatDevice_CiA402 inherits from _EthercatDevice_CommonDriver.
For more detailed information about EtherCAT Device Class, please refer to EtherCAT Library API User Manual – QEC.
1.2.1 Drives and Motion Control
The device control function block controls all functions of the drive (drive function and power section). It is divided into device control of the state machine and the operation mode function.
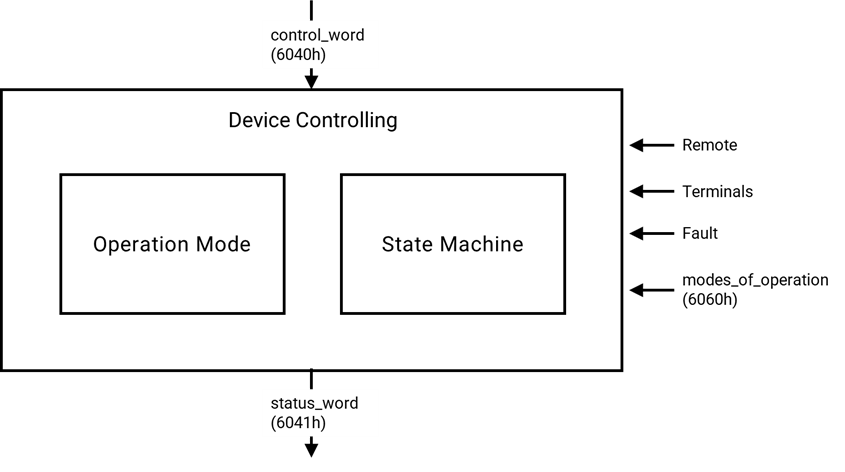
The controlword can control the state of the drive.
The state of the drive is shown in the statusword.
In remote mode, the device is controlled directly from the CANopen network by PDO and SDO.
The state machine is controlled externally by the controlword and external signals. The write access to the controlword is controlled by the optional hardware signal ‘Remote’. The state machine is also controlled by internal signals like faults and modes of operation.
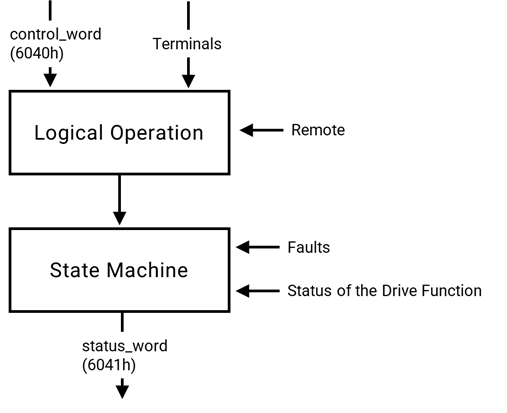
1.2.2 State machine
The state machine describes the device status and the possible control sequence of the drive. A single state represents a special internal or external behavior. The state of the drive also determines which commands are accepted. E.g. it is only possible to start a point-to-point move when the drive is in state OPERATION ENABLE.
States may be changed using the controlword and/or according to internal events. The current state can be read using the statusword.

State Description
| State | 説明 |
| Not Ready to Switch On | Drive is initializing or running a self-test. Brake (if present) is applied. Function disabled. |
| Switch On Disabled | Initialization complete, parameters set. High voltage not applied for safety. Function disabled. |
| Ready to Switch On | High voltage may be applied. Drive parameters can be modified. Function disabled. |
| Switched On | High voltage applied. Power amplifier is ready. Drive parameters can be modified. Function disabled. |
| Operation Enable | Fault detected. Drive function disabled. High-voltage switch-off depends on the application. |
| Quick Stop Active | Quick stop executed. Power removed, function disabled. To resume, send Enable Operation. |
| Fault Reaction Active | Fault detected. Quick stop is being executed. Power removed, function disabled. |
| Fault | Fault detected. Drive function disabled. High voltage switch-off depends on application. |
Notes:
- If a command is received that causes a change of state, this command must be processed completely and the new state attained before the next command can be processed.
- ‘Drive function is disabled’ implies no energy is supplied to the motor. This may be achieved by different manufacturers in different ways. Reference values are not processed.
- ‘Drive function is enabled’ implies that energy can be supplied to the motor. The reference values (torque, velocity, position) are processed.
- ‘Fault occurred’ implies that a fault in the drive has occurred. In this case, there is a transition to the state FAULT REACTION ACTIVE. In this state the device will execute a special fault reaction. After the execution of this fault reaction, the device will switch to the state FAULT. This state can only be left by the command ‘Fault Reset’, but only if the fault is not active anymore.
2. 関数
2.1 Initialization-related Functions
Initialization-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
2.2 Control-related Functions
Control-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
2.3 Operation-related Functions
Operation-related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- setTargetPosition()
- setTargetVelocity()
- setTargetTorque()
- setProfileAcceleration()
- setProfileDeceleration()
- setMaxAcceleration()
- setMaxDeceleration()
- setMaxProfileVelocity()
- setMotionProfileType()
- setPositionWindow()
- setPositionWindowTime()
- setPositionOffset()
- setSoftwarePositionLimit()
- setFollowingErrorWindow()
- setPositionPolarity()
- setVelocityWindow()
- setVelocityWindowTime()
- setVelocityThreshold()
- setVelocityOffset()
- setMaxMotorSpeed()
- setVelocityPolarity()
- setTorqueOffset()
- setMaxTorque()
- setPositiveTorqueLimit()
- setNegativeTorqueLimit()
- setQuickStopDeceleration()
- setQuickStopOptionCode()
- setShutdownOptionCode()
- setDisableOperationOptionCode()
- setHaltOptionCode()
- setFaultReactionOptionCode()
- getErrorCode()
- getSupportedDriveModes()
- getMotorResolution()
- getPositionActualValue()
- getVelocityActualValue()
- getTorqueActualValue()
- getCurrentActualValue()
- getPositionDemandValue()
- getPositionDemandInternalValue()
- getPositionActualInternalValue()
- getAdditionalPositionActualValue()
- getFollowingErrorActualValue()
- getVelocityDemandValue()
- getTorqueDemandValue()
- getDigitalInputs()
2.4 Profile Position mode (pp) Related Functions
Profile Position mode (pp) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- pp_SetVelocity()
- pp_SetAcceleration()
- pp_SetDeceleration()
- pp_SetMotionProfileType()
- pp_Run()
- pp_IsTargetReached()
- pp_CheckFollowingError()
- pp_Halt()
- pp_Resume()
2.5 Profile Velocity mode (pv) Related Functions
Profile Velocity mode (pv) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- pv_SetAcceleration()
- pv_SetDeceleration()
- pv_SetMotionProfileType()
- pv_Run()
- pv_IsTargetReached()
- pv_CheckZeroSpeed()
- pv_CheckMaxSlippageError()
- pv_Halt()
- pv_Resume()
2.6 Profile Torque mode (tq) Related Functions
Profile Torque mode (tq) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- tq_SetTorqueSlope()
- tq_SetTorqueProfileType()
- tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent()
- tq_SetMotorRatedTorque()
- tq_Run()
- tq_IsTargetReached()
- tq_Halt()
- tq_Resume()
2.7 Homing mode (hm) Related Functions
Homing mode is the process by which a drive seeks the home position, also referred to as the datum, reference point, or zero point. This ensures that the motor starts from a known and repeatable position.
Homing can be achieved through various methods, typically using limit switches at the ends of travel or a home switch (zero point switch) in mid-travel. Many homing methods also utilize the index (zero) pulse train from an incremental encoder for precise positioning.
Homing mode (hm) related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- hm_SetHomeOffset()
- hm_SetHomingMethod()
- hm_SetHomingSpeeds()
- hm_SetHomingAcceleration()
- hm_Run()
- hm_IsAttained()
- hm_Stop()
2.8 Function Group “Touch Probe” Related Functions
Touch Probe related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- enableTouchProbe1()
- enableTouchProbe2()
- disableTouchProbe1()
- disableTouchProbe2()
- isTouchProbe1ValueReady()
- isTouchProbe2ValueReady()
- readTouchProbe1Value()
- readTouchProbe2Value()
2.9 Low-level functions for mode-specific flow control
Low-level functions for mode-specific flow control related functions for the EthercatDevice_CiA402 class.
Functions:
- setHaltBit()
- isTargetReached()
- setModeSpecificBit4()
- setModeSpecificBit5()
- setModeSpecificBit6()
- checkModeSpecificBit12()
- checkModeSpecificBit13()
3. Example
3.1 Profile Position (pp) control
Implement position control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Position mode (pp).
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the positive direction.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the negative direction.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PP_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pp_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pp_SetVelocity(100000);
motor.pp_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pp_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
motor.pp_Run(100000, CIA402_PP_RELATIVE, true);
while (motor.pp_IsTargetReached() == 0);
motor.pp_Run(-100000, CIA402_PP_RELATIVE, true);
while (motor.pp_IsTargetReached() == 0);
}3.2 Profile Position (pp) control in cyclic callback
Implement position control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Position mode (pp) in cyclic callback.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the positive direction.
- Move a relative distance of 10,000 units in the negative direction.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 607Ah: Target position
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6064h: Position actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
#define STATE_SET_COMMAND (0)
#define STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET (1)
#define STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR (2)
#define STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED (3)
int state = STATE_SET_COMMAND;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
switch (state) {
case STATE_SET_COMMAND:
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetPosition(100000 * toggle - 100000 * !toggle);
motor.setModeSpecificBit6(true);
motor.setModeSpecificBit5(false);
motor.setModeSpecificBit4(true);
state = STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET;
break;
case STATE_CHECK_ACK_SET:
if (motor.checkModeSpecificBit12()) {
motor.setModeSpecificBit4(false);
state = STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR;
}
break;
case STATE_CHECK_ACK_CLEAR:
if (motor.checkModeSpecificBit12() == 0)
state = STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED;
break;
case STATE_WAIT_TARGET_REACHED:
if (motor.pp_IsTargetReached())
state = STATE_SET_COMMAND;
break;
}
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PP_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pp_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pp_SetVelocity(100000);
motor.pp_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pp_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.3 Profile Velocity (pv) control
Implement velocity control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Velocity mode (pv).
- Move in the positive direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
- Move in the negative direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PV_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.pv_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pv_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pv_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
motor.pv_Run(1000);
while (motor.pv_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
motor.pv_Run(-1000);
while (motor.pv_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
}3.4 Profile Velocity (pv) control in cyclic callback
Implement velocity control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Velocity mode (pv).
- Move in the positive direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
- Move in the negative direction at a speed of 1,000 units per second for 3 seconds.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 60FFh: Target velocity
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 606Ch: Velocity actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int toggle = 0;
int cycle_count = 3000;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (++cycle_count < 3000)
return;
cycle_count = 0;
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetVelocity(1000 * toggle - 1000 * !toggle);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_PV_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60FF0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x606C0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000);
motor.enable();
motor.pv_SetMotionProfileType(0);
motor.pv_SetAcceleration(5000);
motor.pv_SetDeceleration(5000);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.5 Profile Torque (tq) control
Implement torque control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Torque mode (tq).
- Maintain a positive torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
- Maintain a negative torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_TQ_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.tq_SetTorqueProfileType(0);
motor.tq_SetTorqueSlope(200);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedTorque(0);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent(0);
}
void loop() {
motor.tq_Run(50);
while (motor.tq_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
motor.tq_Run(-50);
while (motor.tq_IsTargetReached() == 0);
delay(3000);
}3.6 Profile Torque (tq) control in cyclic callback
Implement torque control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice supporting Profile Torque mode (tq).
- Maintain a positive torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
- Maintain a negative torque of 50 units for 3 seconds.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 6071h: Target torque
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6077h: Torque actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int toggle = 0;
int cycle_count = 3000;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (++cycle_count < 3000)
return;
cycle_count = 0;
toggle = !toggle;
motor.setTargetTorque(50 * toggle - 50 * !toggle);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_TQ_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60710010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60770010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000);
motor.enable();
motor.tq_SetTorqueProfileType(0);
motor.tq_SetTorqueSlope(200);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedTorque(0);
motor.tq_SetMotorRatedCurrent(0);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.7 Homing (hm) operation
Initiate the homing method 33 operation on a CiA 402 compliant EtherCAT SubDevice.
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_HOMING_MODE);
master.start();
motor.enable();
motor.hm_SetHomingMethod(CIA402_HM33);
motor.hm_SetHomeOffset(0);
motor.hm_SetHomingSpeeds(100, 20);
motor.hm_SetHomingAcceleration(100);
motor.hm_Run();
while (motor.hm_IsAttained() == CIA402_HM_RUNNING);
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.8 Cyclic synchronous position (CSP) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Position (CSP) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target position is incremented by 1,000 units in each cycle.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 607Ah: Target position
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6064h: Position actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int32_t position = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
motor.setTargetPosition(position += 1000);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CSP_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x607A0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60640020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetPosition(position = motor.getPositionActualValue());
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.9 Cyclic synchronous velocity (CSV) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Velocity (CSV) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target velocity is incremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches 3,000 units.
- The target velocity is decremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches -3,000 units.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 60FFh: Target velocity
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 606Ch: Velocity actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int32_t velocity = 0;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (abs(velocity) >= 3000)
toggle = !toggle;
velocity = velocity + toggle - !toggle;
motor.setTargetVelocity(velocity);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CSV_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60FF0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x606C0020);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetVelocity(0);
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}3.10 Cyclic synchronous torque (CST) control in cyclic callback
Implement Cyclic Synchronous Torque (CST) control on a CiA 402 EtherCAT SubDevice.
- The target torque is incremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches 50 units.
- The target torque is decremented by 1 unit each cycle until it reaches -50 units.
To operate in cyclic callback, the relevant objects must be mapped to PDOs as follows:
- Output PDO (RxPDO)
- Object 6040h: Controlword
- Object 6071h: Target torque
- Input PDO (TxPDO)
- Object 6041h: Statusword
- Object 6077h: Torque actual value
Here is the example code.
#include "Ethercat.h"
EthercatMaster master;
EthercatDevice_CiA402 motor;
int16_t torque = 0;
int toggle = 0;
void MyCyclicCallback()
{
if (motor.getCiA402State() != CIA402_OPERATION_ENABLED)
return;
if (abs(torque) >= 50)
toggle = !toggle;
torque = torque + toggle - !toggle;
motor.setTargetTorque(torque);
}
void setup() {
master.begin();
motor.attach(0, master);
motor.setDc(1000000);
motor.setCiA402Mode(CIA402_CST_MODE);
/* RxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x01, 0x60400010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1601, 0x02, 0x60710010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1601, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C12, 0x01, 0x1601);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C12, 0x00, 1);
/* TxPDO mapping configuration. */
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 0);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x01, 0x60410010);
motor.sdoDownload32(0x1A01, 0x02, 0x60770010);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1A01, 0x00, 2);
motor.sdoDownload16(0x1C13, 0x01, 0x1A01);
motor.sdoDownload8(0x1C13, 0x00, 1);
master.attachCyclicCallback(MyCyclicCallback);
master.start(1000000, ECAT_SYNC);
motor.setTargetTorque(0);
motor.enable();
}
void loop() {
// ...
}付録
A.1 エラーリスト
ほとんどの関数では、返される値が0未満の場合、エラーであることを示し、その値はエラー・コードを表します。エラー・コードがある場合は、エラーの原因と修正処置を下記で確認できます。
| 定義 | コード |
ECAT_SUCCESS | 0 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_INIT_FAIL | -100 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_GET_VERSION_FAIL | -101 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_VERSION_MISMATCH | -102 |
ECAT_ERR_MODULE_GENERIC_TRANSFER_INIT_FAIL | -103 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_DOWNLOAD_SETTINGS_FAIL | -200 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SET_DEVICE_SETTINGS_FAIL | -201 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_GROUP_INFO_FAIL | -202 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_MASTER_INFO_FAIL | -203 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GET_DEVICE_INFO_FAIL | -204 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SET_GROUP_SETTINGS_FAIL | -205 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_MAPPING_INIT_FAIL | -206 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_INTERRUPT_INIT_FAIL | -207 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACTIVE_FAIL | -208 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_INITCMDS_FAIL | -209 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NO_DEVICE | -210 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_INIT_FAIL | -300 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_REQUEST_FAIL | -301 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_BUSY | -302 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_TIMEOUT | -303 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_ERROR | -304 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ACYCLIC_WRONG_STATUS | -405 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GENERIC_SEND_FAIL | -400 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_GENERIC_RECV_FAIL | -401 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_BEGIN | -1000 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WRONG_BUFFER_SIZE | -1001 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_REDUNDANCY_NO_DC | -1002 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAIL | -1003 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_OSLAYER_INIT_FAIL | -1004 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NIC_INIT_FAIL | -1005 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_BASE_INIT_FAIL | -1006 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CIA402_INIT_FAIL | -1007 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SETUP_PDO_FAIL | -1008 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SCAN_NETWORK_FAIL | -1009 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_START_MASTER_FAIL | -1010 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CYCLETIME_TOO_SMALL | -1011 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_DUMP_OUTPUT_PDO_FAIL | -1012 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CONFIG_DEVICE_FAIL | -1013 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CONFIG_MAPPING_FAIL | -1014 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WAIT_BUS_SYNC_TIMEOUT | -1015 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WAIT_MASTER_SYNC_TIMEOUT | -1016 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_CYCLIC_START_FAIL | -1017 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_WRONG_BUFFER_POINTER | -1018 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_INIT_FAIL | -1050 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_ENI_MISMATCH | -1051 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_STOPPED | -1100 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_STARTED | -1101 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_PREOP | -1102 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_SAFEOP | -1103 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_NOT_IN_OP | -1104 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_II_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1200 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_IP_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1201 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_PS_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1202 |
ECAT_ERR_MASTER_SO_TRANSITION_FAIL | -1203 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_EXIST | -2000 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_ATTACH | -2001 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_MAILBOX | -2002 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_DC | -2003 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_WRONG_INPUT | -2004 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAIL | -2005 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID_MISMATCH | -2006 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PRODUCT_CODE_MISMATCH | -2007 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_SUCH_FUNCTION | -2008 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FUNCTION_NOT_INIT | -2009 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_BUSY | -2010 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_TIMEOUT | -2011 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_NO_DATA | -2012 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_SII_READ_FAIL | -2100 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_SII_WRITE_FAIL | -2101 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PDO_NOT_EXIST | -2200 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_PDO_OUT_OF_RANGE | -2201 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2300 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2310 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_TIMEOUT | -2311 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_ERROR | -2312 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL | -2313 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_READ_FAIL | -2314 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_FOE_WRITE_FAIL | -2315 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_SDO_NOT_SUPPORT | -2400 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_SDO_INFO_NOT_SUPPORT | -2401 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_BUSY | -2410 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2411 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_TIMEOUT | -2412 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_COE_ERROR | -2413 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NOT_EXIST | -2500 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_ADD_FAIL | -2501 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_TYPE_MISMATCH | -2502 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_MODE_SUPPORT | -2503 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_WRONG_MODE | -2504 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_MODE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2505 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_CHANGE_WRONG_STATE | -2506 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_WRITE_OBJECT_FAIL | -2507 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_SUCH_TOUCH_PROBE | -2580 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_CIA402_NO_SUCH_TOUCH_PROBE_SOURCE | -2581 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_NOT_SUPPORT | -2600 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_NO_SUCH_PORT | -2601 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_TOO_MUCH_CONTENT | -2602 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_BUSY | -2610 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_REQUEST_FAIL | -2611 |
ECAT_ERR_DEVICE_EOE_TIMEOUT | -2612 |
ECAT_ERR_GROUP_WRONG_INPUT | -3000 |
ECAT_ERR_GROUP_NOT_ATTACH | -3001 |
A.2 エラーの説明と修正処置
エラーコードの詳細と修正処置
A.3 SDO Abort Code
ETG.1000.6に定義されたCoE SDOアボート・コード:
| Value | Meaning |
| 0x05030000 | トグル・ビットは変更されていません |
| 0x05040000 | SDOプロトコルのタイムアウト |
| 0x05040001 | クライアント/サーバーのコマンドの指定子が無効であるか、不明です。 |
| 0x05040005 | メモリ不足です |
| 0x06010000 | オブジェクトへのアクセスがサポートされていません |
| 0x06010001 | 書き込み専用オブジェクトへ読み取りを試みます |
| 0x06010002 | 読み取り専用オブジェクトに書き込みを試みます |
| 0x06010003 | サブインデックスに書き込むことはできません。書き込みアクセスの場合はSI0を0にする必要があります |
| 0x06010004 | SDO完全アクセスは、ENUMオブジェクト・タイプのような可変長のオブジェクトではサポートされていません |
| 0x06010005 | オブジェクトの長さがメールボックスのサイズを超えています |
| 0x06010006 | オブジェクトがRxPDOにマップされ、SDOダウンロードがブロックされました |
| 0x06020000 | オブジェクトがオブジェクト・ディレクトリに存在しません |
| 0x06040041 | オブジェクトは PDO にマッピングできません |
| 0x06040042 | マップされるオブジェクトの数と長さは PDOの長さを超えます |
| 0x06040043 | 一般的な媒介変数の非互換性理由 |
| 0x06040047 | デバイスの一般的な内部非互換性 |
| 0x06060000 | ハードウェア・エラーによりアクセスに失敗しました |
| 0x06070010 | データ型が一致せず、サービス変数の長さが一致しません |
| 0x06070012 | データ型が一致せず、サービス変数の長さが長すぎます |
| 0x06070013 | データ型が一致せず、サービス変数の長さが短すぎます |
| 0x06090011 | サブインデックスが存在しません |
| 0x06090030 | 媒介変数の値の範囲を超えました(書き込みアクセスの場合のみ) |
| 0x06090031 | 書き込まれた変数の値が高すぎます |
| 0x06090032 | 書き込まれた変数の値が低すぎます |
| 0x06090036 | 最大値が最小値より小さいです |
| 0x08000000 | 一般的なエラーです |
| 0x08000020 | データをアプリケーションに転送または保存することはできません。 注: これは、理由の詳細が特定できない場合の一般的な中止コードです。より詳細な中止コード(0x08000021、0x08000022)のいずれかを使用することをお勧めします。 |
| 0x08000021 | ローカル制御のため、データをアプリケーションに転送または保存することはできません。 注: 「ローカル制御」とは、アプリケーション固有の理由を意味します。 ESM固有の制御を意味するものではありません。 |
| 0x08000022 | 現在のデバイスの状態のため、データをアプリケーションに転送または保存できません。 注: 「デバイスの状態」とは、ESMの状態を意味します。 |
| 0x08000023 | オブジェクト・ディクショナリの動的生成が失敗するか、オブジェクト・ディクショナリが存在しません |
A.4 Data Type
ETG.1000.6で定義されている基本データ型:
| インデックス (hex) | オブジェクト・タイプ | 名前 |
| 0001 | DEFTYPE | BOOLEAN |
| 0002 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER8 |
| 0003 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER16 |
| 0004 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER32 |
| 0005 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED8 |
| 0006 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED16 |
| 0007 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED32 |
| 0008 | DEFTYPE | REAL32 |
| 0009 | DEFTYPE | VISIBLE_STRING |
| 000A | DEFTYPE | OCTET_STRING |
| 000B | DEFTYPE | UNICODE_STRING |
| 000C | DEFTYPE | TIME_OF_DAY |
| 000D | DEFTYPE | TIME_DIFFERENCE |
| 000F | DEFTYPE | DOMAIN |
| 0010 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER24 |
| 0011 | DEFTYPE | REAL64 |
| 0012 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER40 |
| 0013 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER48 |
| 0014 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER56 |
| 0015 | DEFTYPE | INTEGER64 |
| 0016 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED24 |
| 0018 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED40 |
| 0019 | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED48 |
| 001A | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED56 |
| 001B | DEFTYPE | UNSIGNED64 |
| 001D | DEFTYPE | GUID |
| 001E | DEFTYPE | BYTE |
| 002D | DEFTYPE | BITARR8 |
| 002E | DEFTYPE | BITARR16 |
| 002F | DEFTYPE | BITARR32 |
A.5 About CiA DSP 402
The CiA DSP 402 represents the standardized CANopen device profile for digital controlled motion products like servo controllers, frequency converters or stepper motors.
All the devices mentioned above use communication techniques which conform to those described in the CiA Draft Standard DS 301 (CANopen Application Layer and Communication Profile). This document should be consulted in parallel to CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
REFERENCES
- ISO 7498, 1984, Information Processing Systems – Open Systems Interconnection – Basic Reference Model
- ISO 11898-1, 1999, Road Vehicles, Interchange of Digital Information – Controller Area Network (CAN) for high-speed Communication
- CiA DS 301, CANopen Application Layer and Communication Profile, Version 4.02, February 2002
- CiA DS 401, CANopen Device Profile I/O Modules, Version 2.1, May 2002
- DRIVECOM Profil Antriebstechnik/Profil 21
- DRIVECOM Profil Antriebstechnik/Servo 22, Jan. 1994
DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATION
| Abbr. | 定義 |
| CAN | Controller Area Network |
| CiA | CAN in Automation e. V. |
| COB | Communication Object (CAN message). A unit of transportation in a CAN network. Data must be sent across a network inside a COB. |
| COB-ID | COB-Identifier. Identifies a COB uniquely in a network. The identifier determines the priority of that COB in the MAC sub-layer too. |
| PDO | Process Data Object. Object for data exchange between several devices. |
| SDO | Service Data Object. Peer-to-peer communication with access to the object dictionary of a device. |
| pp | Profile Position Mode |
| pv | Profile Velocity Mode |
| vl | Velocity Mode |
| hm | Homing Mode |
| ip | Interpolated Position Mode |
| tq | Profile Torque Mode |
| all | Mandatory for all modes |
| ce | Common entries in the object dictionary |
| dc | Device Control |
| pc | Position Control Function |
A.6 Object Dictionary Entries
All information follows the CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
A.7 Homing Methods
All information follows the CiA® 402-CANopen Drives and Motion Control Profile.
86Duinoリファレンスのテキストは、Arduinoリファレンスを改変したもので、Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0ライセンスに基づいてライセンスされています。リファレンス内のコードサンプルはパブリックドメインとして公開されています。
詳細情報やサンプルのご要望については、info@icop.com.tw までメールをお送りいただくか、最寄りの ICOP 支店 までお電話いただくか、ワールドワイド正規販売代理店までお問い合わせください。